 LEARN
LEARN
What is sustainability? How is sustainability applied in a practical, meaningful way? How can sustainability be integrated into an organization’s culture and daily operations? Understanding and exploring the answers to these questions is an important step to successfully implementing sustainability principles.
What is Sustainability?

|
|
What does sustainability mean to you?
-
Anonymous
- lxbfYeaa lxbfYeaa, 1
-
Anonymous
- lxbfYeaa lxbfYeaa, 1
- lxbfYeaa lxbfYeaa, 1
Share what sustainability means to you and your organization.
How are sustainability principles applied in a practical, meaningful way?
Airports and organizations around the world have successfully implemented sustainability programs without creating a financial burden or causing disruption in operations. Along with benefiting their communities and the environment, airports are finding that sustainability makes good business sense. Airports that have adopted sustainable practices have found substantial benefits including reduced capital asset life cycle costs, reduced operating costs, better customer service and satisfaction, and enhanced relationships with their neighbors.
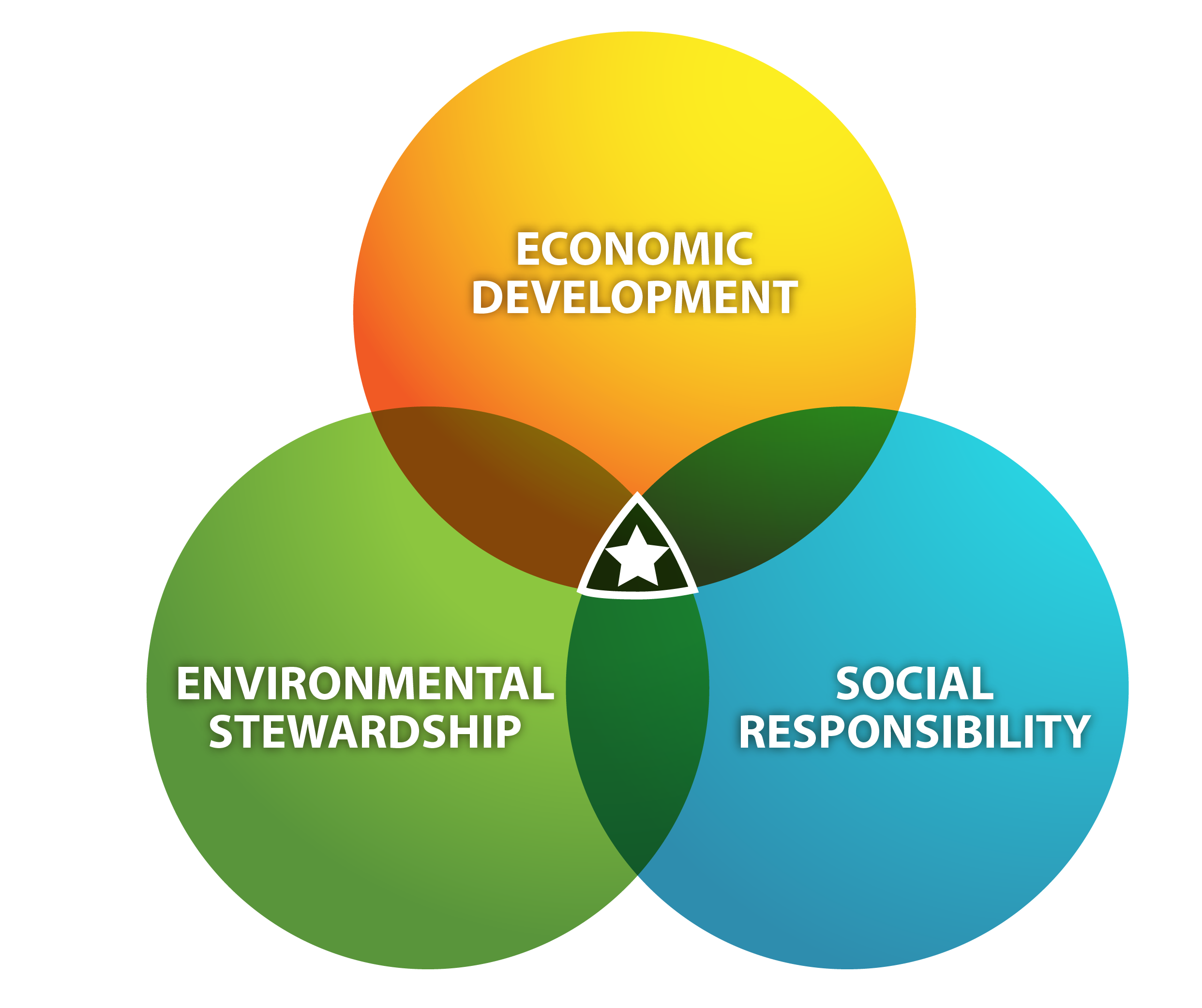
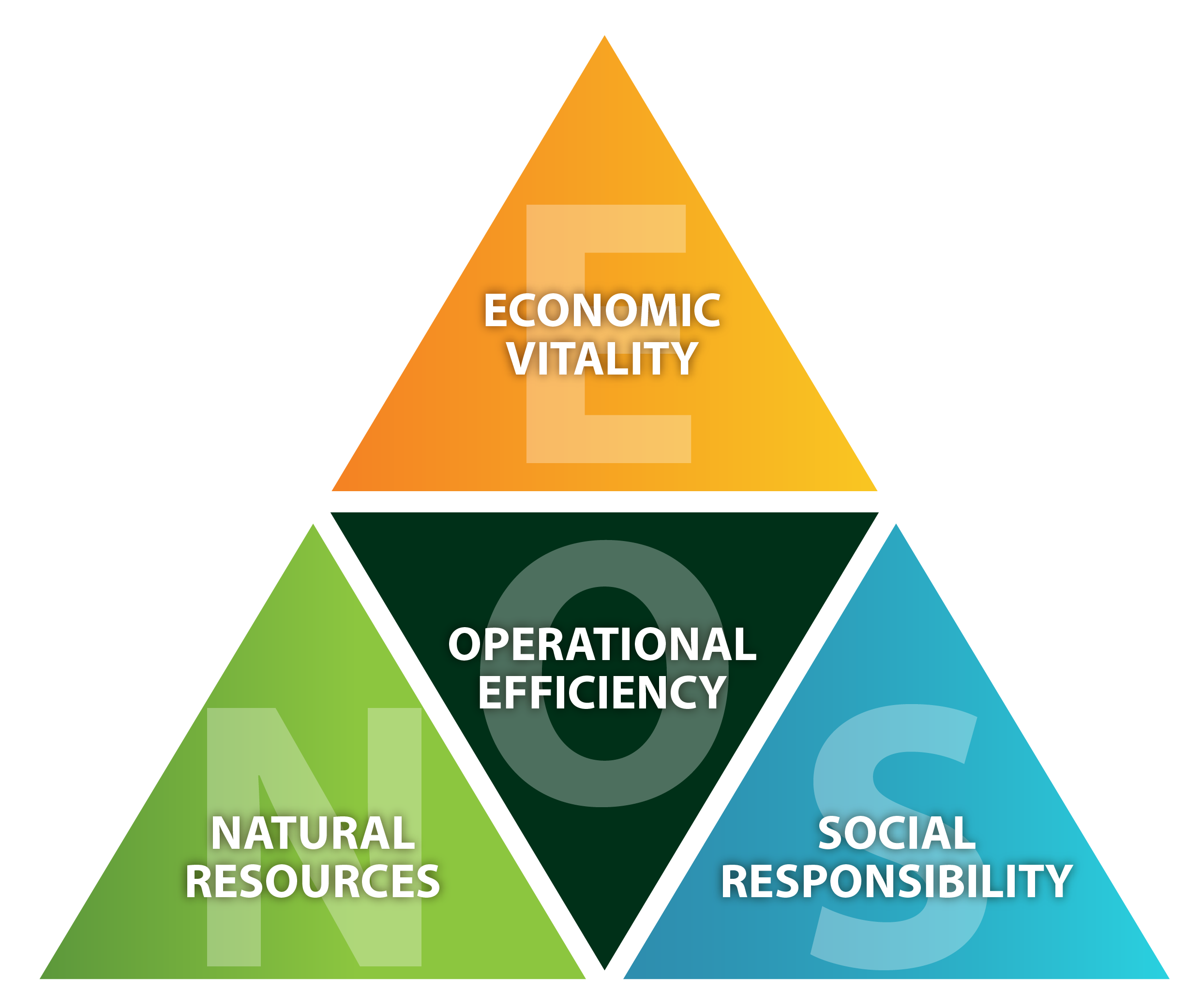
Connecting sustainability to other goals within the airport is critical to developing a successful program. In many cases, sustainability efforts begin by finding initiatives that save money while stimulating economic growth, protecting the environment, and improving social responsibility. In addition, sustainability is a useful tool to engage stakeholders, create partnerships, improve customer satisfaction, and draw business to the airport. Creating short-term successes through sustainability and showcasing those achievements helps to build support for future sustainability efforts.
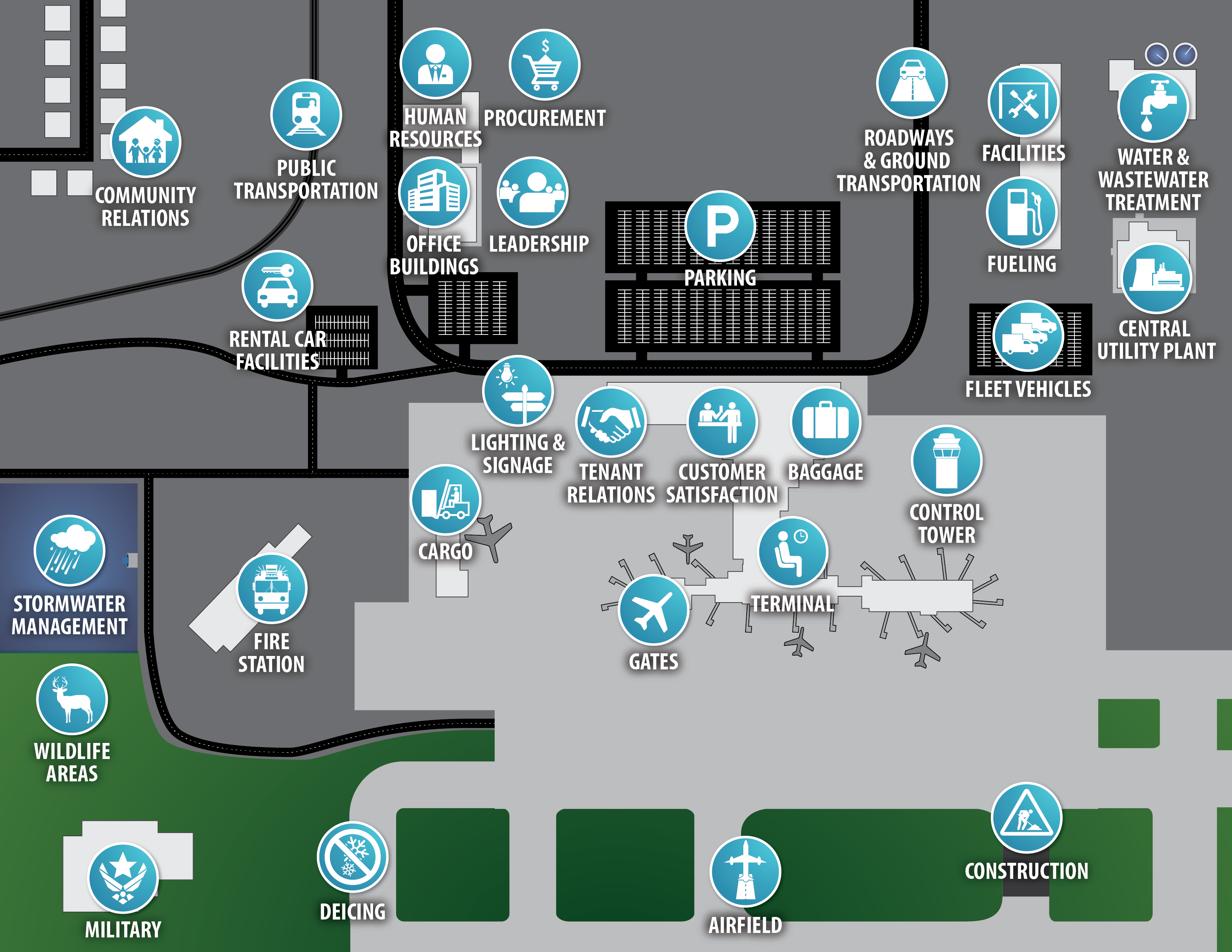
Click on the blue icons on the map below to see a list of initiatives that are applicable to that location and function. The figure below highlights some practices that have been successful at airports around the world. These practices are examples of ways to integrate sustainability into the airport’s operations. This map is also located on the SUSTAINABLE PRACTICES page to improve search results.
Connecting sustainability to other goals within the airport is critical to developing a successful program. In many cases, sustainability efforts begin by finding initiatives that save money while stimulating economic growth, protecting the environment, and improving social responsibility. In addition, sustainability is a useful tool to engage stakeholders, create partnerships, improve customer satisfaction, and draw business to the airport. Creating short-term successes through sustainability and showcasing those achievements helps to build support for future sustainability efforts.
Click on the blue icons on the map below to see a list of initiatives that are applicable to that location and function. The figure below highlights some practices that have been successful at airports around the world. These practices are examples of ways to integrate sustainability into the airport’s operations. This map is also located on the SUSTAINABLE PRACTICES page to improve search results.
How can sustainability be integrated into an organization’s culture and daily operations?
Although sustainability initiatives can be implemented on individual basis, integrating sustainability into our culture and day-to-day business practices is the ultimate goal of the Triple Bottom Line and EONS. A comprehensive sustainability program will empower employees, customers, tenants and other stakeholders to consider sustainability is all decisions, both professional and personal. Strategies that may be helpful in achieving this goal include:
- Providing effective communication and education programs to help people understand how to apply sustainability in their jobs and lives
- Setting top-level, organization-wide goals for sustainability
- Engaging employees and stakeholders responsible for implementation and allowing them to help select activities and performance indicators
- Providing incentives for employees and stakeholders to participate in sustainability activities
- Linking annual performance appraisals to achievement of sustainability goals
- Creating a “Sustainability Manager” position and/or appointing a sustainability champion(s)
- Achieving and showcasing executive level commitment to sustainability
- Measuring and communicating progress toward sustainability goals
- Incorporating sustainability components into existing management systems
- Formalizing a sustainability policy and best management practices and procedures
- Celebrating sustainability successes


The findings of the Brundtland Commission are also commonly used as a definition of sustainability and sustainable development. The Brundtland Commission, also known as the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED), was convened by the United Nations (UN) in 1983 to address a growing concern “about the accelerating deterioration of the human environment and natural resources and the consequences of that deterioration for economic and social development.” In establishing the commission, the UN General Assembly recognized that environmental problems were global in nature and determined that it was in the common interest of nations to establish policies for sustainable development. The exponential growth in the world’s population requires the implementation of global resource management to ensure that resources are available for future generations. In 1987, the Brundtland Commission released the following definition of sustainable development:
Many airports find that they already have existing activities or programs that fall within the sustainability realm, even if they do not have a formal sustainability program. Examples include “Buy Local”, “Recycling”, or “Stockpile and Reuse Construction Materials”. These are common-sense activities that fall under the umbrella of sustainability. Identifying a definition of sustainability can be an important first step in starting or enhancing a sustainability program.